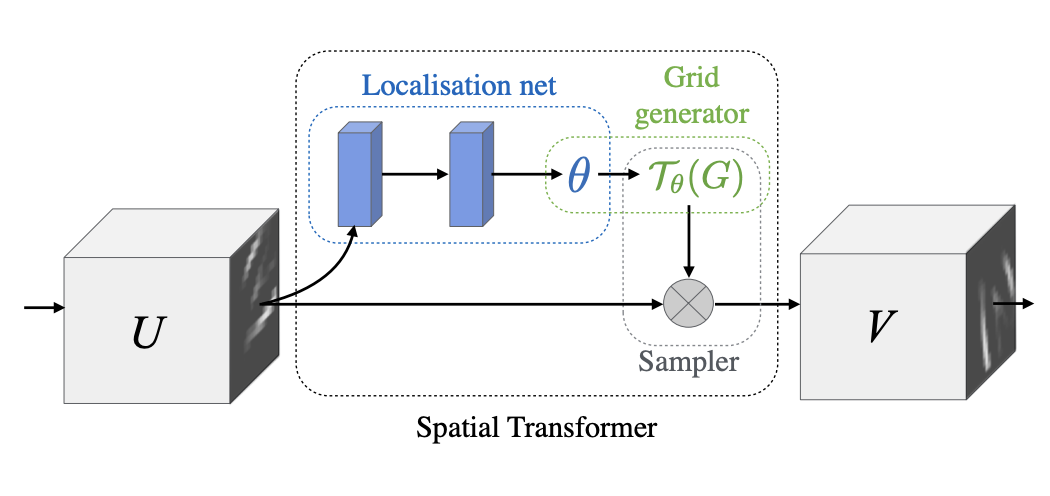
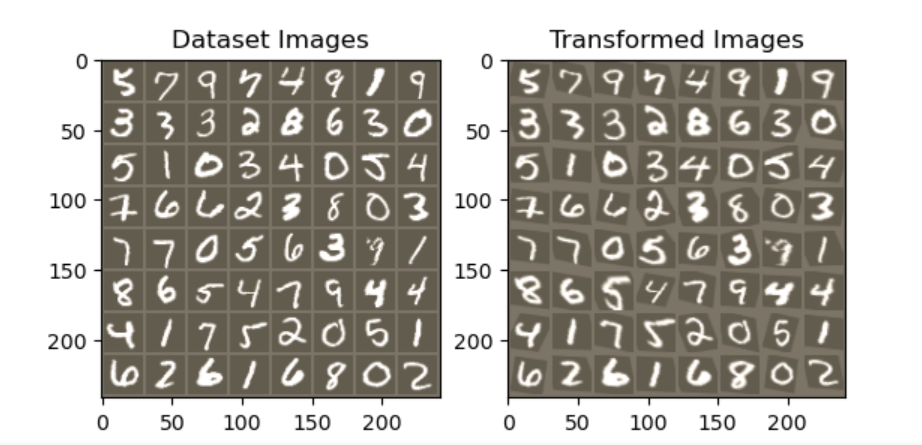
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
| from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='.', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])), batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='.', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])), batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
self.localization = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=8, kernel_size=7),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(8, 10, kernel_size=5),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
self.fc_loc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(10 * 3 * 3, 32),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(32, 3 * 2)
)
self.fc_loc[2].weight.data.zero_()
self.fc_loc[2].bias.data.copy_(torch.tensor([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], dtype=torch.float))
def stn(self, x):
xs = self.localization(x)
xs = xs.view(-1, 10 * 3 * 3)
theta = self.fc_loc(xs)
theta = theta.view(-1, 2, 3)
grid = F.affine_grid(theta=theta, size=x.size())
x = F.grid_sample(x, grid)
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.stn(x)
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
model = Net().to(device)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
def train(epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % 500 == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
def test():
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item()
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'
.format(test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
def convert_image_np(inp):
"""Convert a Tensor to numpy image."""
inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
inp = std * inp + mean
inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1)
return inp
def visualize_stn():
with torch.no_grad():
data = next(iter(test_loader))[0].to(device)
input_tensor = data.cpu()
transformed_input_tensor = model.stn(data).cpu()
in_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(input_tensor))
out_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(transformed_input_tensor))
f, axarr = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axarr[0].imshow(in_grid)
axarr[0].set_title('Dataset Images')
axarr[1].imshow(out_grid)
axarr[1].set_title('Transformed Images')
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(1, 20 + 1):
train(epoch)
test()
visualize_stn()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
|